Risk Management
Robust and stress-tested framework
Our robust Risk Management framework and the independence of our risk management function set us apart as a responsible banker. It enables the execution of our strategic priorities without taking on undue financial and non-financial risks. Our risk policies and processes and their effective implementation through technology and governance enabled us to endure and even grow in these highly uncertain and disruptive times. Stress testing is one of the key risk management tools we use to mitigate and manage the existing as well as emerging risks.
HDFC Bank’s Risk Management Framework
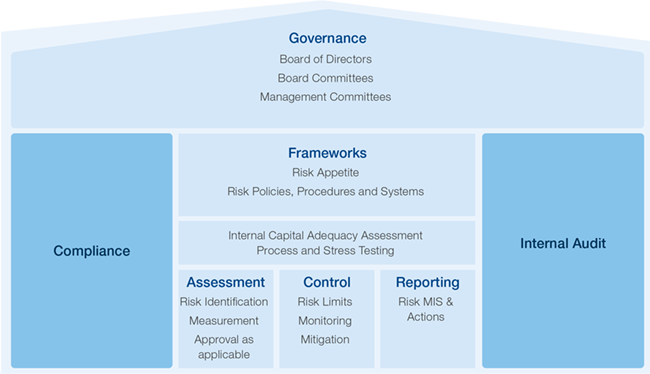
Risk Governance
Our Board of Directors is responsible for managing comprehensive risks. The Risk Policy & Monitoring Committee (RPMC), constituted by the Board, oversees the implementation of our risk strategy. The RPMC guides the development of our policies, procedures and systems and evaluates their adequacy and appropriateness to the changing business conditions, as well as our risk appetite.
The Chief Risk Officer (CRO) heads the independent Risk Management Group (RMG). The CRO interacts regularly with the members of the RPMC. The RMG is primarily responsible for implementing the risk strategy approved by the Board, and developing policies, procedures and systems for identifying, measuring, monitoring, assessing and managing risks.
Risk frameworks and their implementation
The nature of our business and business activities, along with the regulatory environment and external environment at large, exposes us to several types of risks. For us, the keys risks are credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, cyber security and data risk. Our operations expose us to compliance and reputation risk. We are also exposed to ESG risks. We have put in place an aggregate risk appetite framework. In addition, the appetites for individual risk types are operationalised through risk-specific policies, limits and triggers.
We also have a structured management framework in the Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process (ICAAP) to identify, assess and manage all risks that may have a material adverse impact on our business/financial position/capital adequacy.
Risk exposures are regularly captured and reported to the relevant levels of management for initiation of appropriate mitigation measures. We also continuously evaluate the efficacy of existing risk model assumptions and parameters and refine the models to keep up with the changing times.
We have an Internal Audit Department which is responsible for independently evaluating the adequacy and effectiveness of all internal controls, risk management, governance systems and processes.
We have separated the Risk, Audit and Compliance functions from the Business functions to create a strong culture of checks and balances and to eliminate any possible conflict of interest between revenue generation, and risk management and control.
Key risk management initiatives
Evolving stress testing scenarios
In addition to the existing suite of standard stress scenarios, we are conducting stress testing based on topical themes driven by prevailing trends such as geopolitical/macroeconomic/sectoral, among others. These stress tests are conducted focusing on specific areas of portfolio and the results act as early warning alerts/signals for taking actions, if any. Some of the topical themes relevant for the present times include the evolving geopolitical turmoil in Europe due to the Russia-Ukraine conflict, commodity price shocks, and possible shift in key macroeconomic variables in the medium term.
Russia-Ukraine conflict
We analysed both direct and indirect impact of the conflict on our portfolio. The situation remains fluid globally, and there is uncertainty regarding the final outcome from a geopolitical as well as a financial market standpoint. Stress testing of our portfolio considering the current information did not indicate any significant risk. We continue to closely monitor the situation, to pre-empt and manage the risk and its outcomes.
Sri Lanka’s sovereign default
With continuous and robust monitoring of country risk exposures and stress testing, we have proactively taken steps to limit our exposure to Sri Lanka. Although the impact of the default is unlikely to be material for the Bank, we are keeping a close eye on the situation.
Increasing focus on non-financial risks
We believe a lot more can be done in the area of researching, analysing, monitoring and mitigating nonfinancial risks such as operational, technology and reputation, among others. Accordingly, we are elevating deliberations of non-financial risks in the RPMC/Board. We are also in the process of enhancing policies, procedures and risk assessment framework for such non-financial risks.
Leveraging technology
In line with our technology transformation agenda, we are also automating our risk management processes. We believe it will increase efficiencies, enhance accuracy of information, and enable maintenance of adequate audit trail for reviews.
Credit Risk


The risk which arises from default by borrowers in their terms of contract with the Bank, especially failure to make payments or repayments.
Mitigation
An independent Credit Group headed by Chief Credit officer oversees the underwriting functions and approvals across retail and wholesale credit functions. It ensures that the credit underwriting and portfolio management policies are aligned with the Board approved credit appetite. There are robust policies and processes for managing credit risk in both retail and wholesale businesses, mainly through our target defined market, credit approval process, postdisbursement monitoring and remedial management procedures.
Strategies
Maintaining healthy asset quality with optimal risk-reward considerations.
Capitals Impacted

Market Risk


The risk of potential loss on account of adverse changes in market variables which affect the value of financial instruments held by the Bank.
These instruments are primarily held for trading or for management of statutory reserves.
Examples of such market instruments are debt securities, equities, foreign exchange and derivative instruments.
Mitigation
A well-defined Board approved Market Risk Policy, Investment Policy, Foreign Exchange Trading Policy and Derivatives Policy along with robust control activities caps the risk at trading desk level and also at securities level, through trading risk limits in line with the Bank’s risk appetite.
The market risk is also evaluated at portfolio level and controls are implemented to mitigate the risk.
Strategies
Optimising profitability of mark-to-market products within the constraints of liquidity and market risk appetite of the Bank.
Capitals Impacted

Compliance Risk


The risk of legal or regulatory sanctions, as a result of failure to comply with applicable laws, regulations and standards.
Mitigation
Comprehensive Board-approved Compliance policy in place which is reviewed on an annual basis.
The Compliance function tracks and reviews compliance with regulatory guidelines.
Enhancing the compliance culture within the organisation through an intricate and comprehensive internal control framework along with other measures.
Strategies
Strengthening our Compliance checks and balances and ensuring businesses work within the contours of regulation.
Capitals Impacted

Operational Risk


Operational risk arises from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events. It includes risk of loss due to legal risk.
Mitigation
A Board-approved governance structure is in place with detailed framework and processes for managing operational risk. Under the framework, the Bank has three lines of defence namely business line (including support and operations), An independent Operational Risk Management Department (ORMD) and Internal Audit to manage, monitor and mitigate Operational risks.
Strategies
Minimising operational losses through risk mitigation mechanisms.
Capitals Impacted

Climate Risk


At a broader level, risks from climate change are typically divided into:
- Physical risks
Economic losses (physical damage to property and assets) from extreme weather events (flood, cyclone, etc). due to climate change.
- Transition risks
– The possible process of adjustment to a low carbon economy and its possible effects on the value of financial assets and liabilities.
Mitigation
An ESG policy framework has been formulated to address this risk.
Evaluation of environmental and social risk is an integral part of our overall credit appraisal and approval process. Long-term financing proposals for large industrial/infrastructure projects (greater than `100 million and tenor above 5 years) are evaluated through the SEMS framework, which requires an assessment of Environmental, Health, Social, and Safety risks in addition to other risks as part of the overall credit appraisal process. We also track and externally verify our carbon emissions to effectively manage and reduce our footprint.
Strategies
We are exploring frameworks to model and assess climate risk. We also continue our endeavour to acquire granular data, further corroborated by BRSR data (from FY23 onwards), and test tools for climate risk assessment and conducting scenario analysis. We are also exploring options to tie-up with data providers.
On the emissions front, we have set ourselves specific targets towards reduction of our GHG emissions.
Capitals Impacted

Liquidity Risk


Liquidity risk is the risk that the Bank may not be able to meet its financial obligations as they fall due, without incurring unacceptable losses.
Mitigation
The Bank's framework for liquidity and interest rate risk management is spelled out in our Asset LiabilityManagement policy. Further, a robust mechanism to comprehensively track cash flow mismatches under normal as well as stressed conditions and critical ratios including Basel III ratios has also been implemented. The Bank has an extensive intraday liquidity risk management framework for monitoring intraday positions during the day.
Strategies
- To maintain healthy liquidity as evidenced in Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR)/Net Stability Funding Ratio (NSFR) in line with our Balance sheet size to tide over any unforeseen stress scenarios.
- Maintaining competitive cost of funds.
Capitals Impacted

Reputation Risk


Any adverse stakeholder and public perception about our Bank may negatively impact our ability to attract and retain customers and may expose us to litigation and regulatory actions.
Mitigation
We communicate with our stakeholders regularly through appropriate engagement mechanisms to address stakeholder expectations and assuage their concerns, if any.
The Bank has identified reputation risk to be a material risk in its ICAAP Policy and an assessment framework has been established to monitor the level of reputation risk.
Strategies
- Delivering superior and seamless customer experience.
- Wide range of products and services.
Capitals Impacted

Information Technology Risk


Risks associated with the use, ownership, operation, involvement, influence, and adoption of IT within an enterprise, as well as business disruption due to technological failures.
Mitigation
There are well defined policies, frameworks, procedures, templates, and risk assessment methodology for IT risk management.
The framework enables risk assessment of IT solutions, entities providing IT and related services and new technology and digital implementation.
Strategies
Ensure alignment of Business and IT Strategies to provide services and superior customer experience.
Making extensive progress on some of the key initiatives that are part of our technology transformation agenda. The key initiatives are Infrastructure stability, Disaster Recovery Resiliency, Security enhancements and monitoring mechanisms.
Capitals Impacted

Cyber Security and Data Risk


Risk of cyber-attacks on the Bank’s systems through hacking, phishing, ransomware and other means, resulting in disruption of our services or theft or leak of sensitive internal data or customer information.
Mitigation
Each cyber security threat including data privacy issue is assessed basis the framework - Identify, Prevent/Protect, Detect, Respond and Recover. Further controls such as firewalls, anti-malware, anti-advance persistent threats, data loss prevention, Red Teaming, Intrusion prevention/detection, digital rights management, 24*7 security operation centre, and forensics solutions, have been put in place.
The international ‘General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)’ has also been implemented across relevant operations. The Bank is compliant with ISO 27001 and PCI DSS standards.
Strategies
Facilitating bank’s growth via secure Digital 2.0 – implemented through Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud technology.
Adapting and updating Cyber Defence framework, using AI/ML to further augment cyber defence capabilities to counter new-age threats.
Increase information security awareness among employees and customers through specific programmes and communications.
Sustaining operational effectiveness and efficiency through secure Work from Home.
Capitals Impacted


Financial Capital

Human Capital

Intellectual Capital

Social & Relationship Capital

Manufactured Capital
